DKIM and DMARC: why they’re important and critical for communications security
Email Spoofing: how attackers pretend to be legitimate senders
Email spoofing is used in both general fraudulent purposes and targeted attacks. This technique is used to convince victims that a message comes from a trusted sender and push them to perform a specific action, such as clicking on a phishing link, transferring money, downloading a malicious file, etc. For added credibility, attackers may copy the design and style of a particular sender’s emails, emphasize the urgency of the task, and employ other Social Engineering techniques.
To combat spoofing, several mail authentication methods have been created that enhance and complement each other: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. In various ways, these mechanisms verify that the message was actually sent from the given address.
The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) standard allows the owner of a mail domain to limit the set of IP addresses that can send messages from this domain, and allows the mail server to verify that the sender’s IP address is authorized by the domain owner. SPF does not check the From header, but the sender’s domain specified in the SMTP, which is used to transmit information about the path of the e-mail between the mail client and the server and is not shown to the recipient.
DKIM solves the problem of sender authentication using a digital signature generated based on a private key stored on the sender’s server.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) is used to check the domain in the From header against a DKIM/SPF validated domain.
What is a DKIM record?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email security standard designed to ensure that messages are not altered while in transit between sending and receiving servers. It uses public key cryptography to sign email with a private key as it leaves a sending server. Destination servers then use a public key published to a domain’s DNS to verify the origin of the message and that the message body has not changed during transit. Once the public key signature is verified by the recipient server, the message passes DKIM and is considered authentic.
Why is a DKIM record important?
Although DKIM is not mandatory, emails signed with DKIM are “more legitimate” for your recipients and are less likely to go into Junk or Spam folders. Spoofing email from trusted domains is a popular technique for malicious spam and phishing campaigns, and DKIM makes it more difficult to spoof email from domains that use it. Mail servers that do not support DKIM signatures are still able to receive signed messages without problems. It is an optional security protocol and DKIM is not a universally adopted standard.
Although not necessary, it is now highly recommended to use DKIM at your DNS whenever possible to authenticate mail from your domain especially in the enterprise environment, ISPs like Gmail use it to check incoming messages.
An additional benefit of DKIM is that ISPs use it to build a reputation on your domain over time when you send emails and improve your delivery practices (low spam and bounce, high engagement).While it’s important to understand what DKIM does, it’s also important to be clear on what it doesn’t solve: using DKIM will ensure that your message hasn’t been altered, but it doesn’t encrypt the content of your message. Many ESPs use TLS to encrypt messages as they move between sender and recipient, but it is still possible to send unencrypted messages if an email server rejects a TLS connection. Once a message has been delivered, the DKIM signature will remain in the email headers but will not encrypt the message content in any way.
How do DKIM records work?
DKIM uses two actions to verify your messages:
- The first action takes place on a server that sends DKIM-signed emails.
- The second takes place on a recipient server that checks DKIM signatures on incoming messages
The whole process is made possible by a private/public key pair. Your private key is kept secret and secure, either on your server or with your ESP, and the public key is added to the DNS records for your domain to broadcast to the world to help verify your messages. Let’s delve a little deeper into how DKIM works on servers that send and receive email.
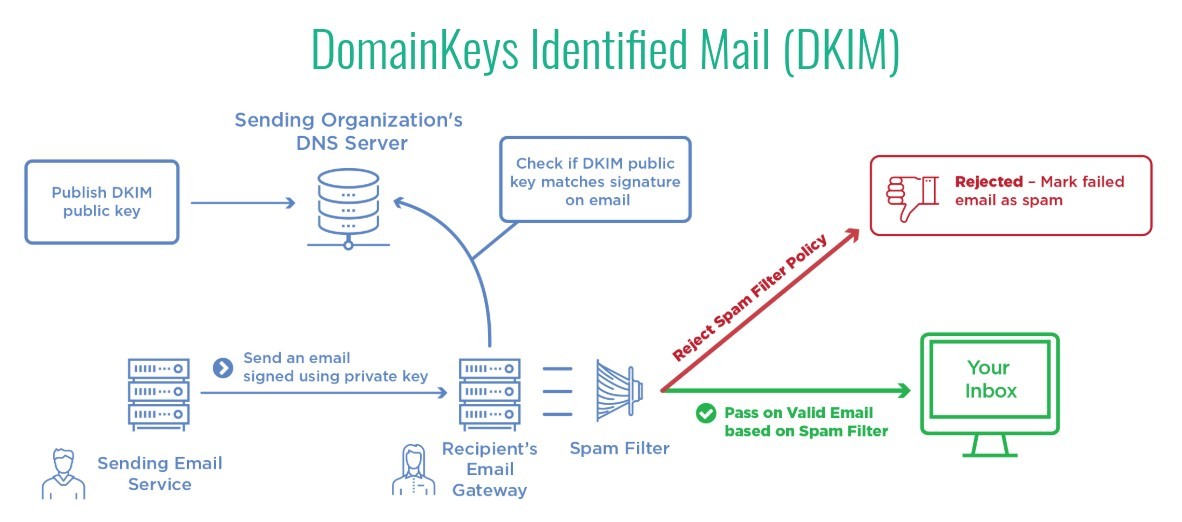
How does DKIM prevent domain spoofing?
DKIM alone does not prevent domain spoofing. You can sign a message using a DKIM key attached to a domain other than the one specified in the “From” header.
However, if you have set a DMARC policy for your domain, the receiving mail server will verify that the DKIM key used to sign the message matches the domain.
What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance, is a protocol created to improve the integrity of the email system. It is used by corporations and government agencies around the world as a means of protecting their business, reputation and customers:
- confirms the identity of the sender, using SPF and DKIM, which are already exposed;
- tells the recipient’s email service what to do with emails that have failed the check;
- asks recipients’ email services to provide reports on where the email came from.
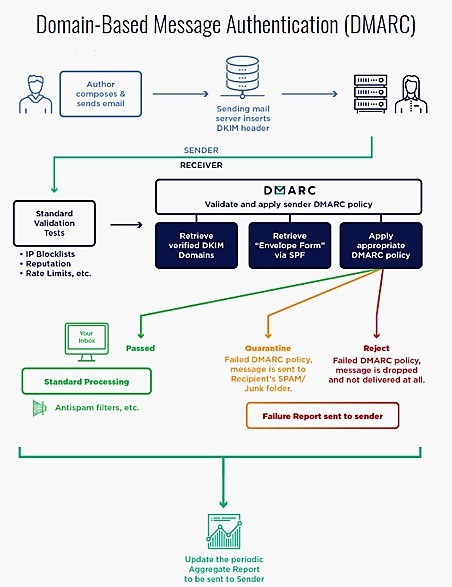
The recipient email service uses SPF and DKIM standards to confirm the identity of the sender. If the receiving email service confirms the identity of the sender, it will forward the email to the recipient’s inbox. If the receiving e-mail service cannot confirm the identity of the sender, it will mark the e-mail as spam.
The most important specifications, therefore, present in the DMARC protocol, such as to make it useful at the same time, are
- the Identifier Alignment with DKIM and SPF standards: the alignment mode (aspf/adkim), in fact, refers to the precision with which sender records are compared with SPF and DKIM signatures.
- reporting. In this case, we have two reporting activities:
- DMARC Policies, DMARC technology allows for three possible settings (or criteria) for handling received messages:
For proper management of the procedures, it is strongly recommended to gradually increase the use of DMARC by employing them in the order just listed.
However, this tool is still not very widespread, the advantages that the implementation of the DMARC protocol offers are many. In fact, it helps protect your business and reputation from fraudulent attacks, reduces customer support costs related to email fraud, improves trust in emails sent from your email address, and allows you to monitor the legitimate and/or fraudulent use of your domains through reporting.
In pure cybersecurity terms, the use of DKIM and DMARC are the best answer to spoofing obviously together with SPF (which we take for granted by now), if you want to do a check to verify the correct insertion and propagation of the DKIM record you can use this tool.
To check if the DMAC record has been correctly configured on your domain you can use the following tool.

Stefano Buzzetti
Head of Information Technology
FLASH NEWS
DOS Group and Adobe
DOS Group’s partnership with Adobe allows us to make the most popular professional digital graphics and photography products available on the market.
The challenges of the tech sector to safeguard the environment
The world of information technology must constantly interface with challenges in the social, economic and political spheres. In a time of great change, however, the well-being of the planet we inhabit must not be neglected.
DOS’s tech lab at the forefront of HP’s product offering
DOS Group’s partnership with HP allows us to provide our customers with a wide range of products from the business line at affordable prices, while maintaining their high quality and professional performance. The new ProBook 440 and 450 series stand out for their speed, efficiency and compact design.
